Precision Medicine with 3D Ultrasound
author: Dr. Azizi et al. / published on July 13, 2023
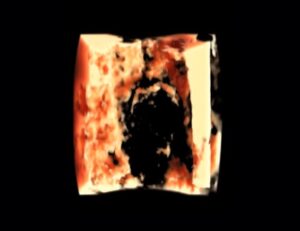
Our 4th video publication with VideoEndocrinology: Precision Medicine with 3D Ultrasound.
read full article

Our 4th video publication with VideoEndocrinology: Precision Medicine with 3D Ultrasound.
read full article
3D Ultrasound & Thyroid Cancer Diagnosis: A Prospective Study
Ghobad Azizi MD, Kirk Faust MD, Lorna Ogden MD, Laura Been MD, Michelle L. Mayo, PA-C, Kele Piper, Carl Malchoff MD
B-mode, or 2-dimensional ultrasound (2D-US), stratifies the malignancy risk of thyroid nodules, but lacks sensitivity. We tested the hypothesis that 3-dimensional ultrasound (3D-US) is superior to 2D-US in predicting malignancy in thyroid nodules.
We prospectively evaluated 344 thyroid nodules using both 2D and 3D ultrasound followed by fine needle aspiration biopsy.
Thyroid nodules were divided into four groups based on the 3D ultrasound appearance of the margins. Bivariate and multivariate analyses were used. A total of 59 patients with 63 thyroid nodules underwent surgery, surgical pathology confirmed 44 thyroid cancers in 40 patients. For 2D-US, irregular margins and microcalcifications were found more frequently in malignant thyroid nodules. Irregular margins on 2D-US had a sensitivity and specificity of 61.4% and 79.3% respectively. Irregular margins on 3D-US had a sensitivity and specificity of 86.4% and 83.3% respectively. Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values were higher for irregular margins on 3D-US, than microcalcifications and irregular margins on 2D-US.
We conclude that the evaluation of thyroid nodule margins by 3D-US distinguishes benign from malignant thyroid nodules with greater sensitivity and specificity than other ultrasound criteria including the evaluation of margins by 2D-US.
Read Article HERE!
read full article

Cancer imaging redefined! Our newest publication: Precision medicine with 3D ultrasound. Diagnosing thyroid cancer with 3D Ultrasound.
read full article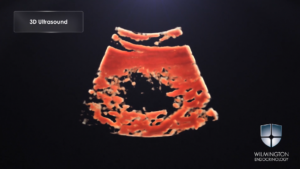
We are thrilled to announce our newest video publication with American Thyroid Association’s VideoEndocrinology™ journal.
read full article
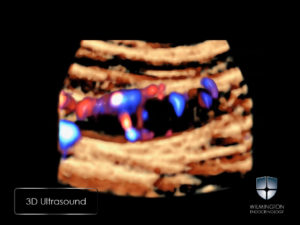
3DParathyroid® has arrived! We are thrilled to announce our newest video publication with American Thyroid Association’s VideoEndocrinology™ journal. This is the first 3D ultrasound publication in diagnosing parathyroid adenomas. This is a cutting edge and non-invasive technology.
Ultrasound technology is becoming an integral part of diagnosing parathyroid adenomas. Careful ultrasound evaluation with b-mode, shear wave elastography, and three-dimensional (3D) of parathyroid adenomas may improve localization and outcome.
read full article

The decision to biopsy small thyroid nodules (TNs) is controversial. Careful ultrasound (US) evaluation with shear wave elastography (SWE) of TN and cervical lymph nodes (LNs) may aid in the decision to biopsy and subsequently influence the extent of surgery. A 46-year-old female presented with TNs and hypothyroidism. Her target TN in the left lobe measured 4.8 mm × 4 mm × 4 mm. Fine needle aspiration biopsy of the left TN and a left neck level 6 LN was diagnostic for papillary thyroid carcinoma. In the left lateral neck posterior to the jugular vein, there was a LN with possible microcalcifications that could not be sampled due to vascular proximity. SWE examination showed high velocity suspicious for metastatic disease. In summary, risk stratification for small TNs and cervical LNs can be difficult. SWE can provide valuable information for assessing the risk for malignancy.
read full article
This study compares shear wave elastography (SWE) and Afirma™ gene expression classifier (GEC) for diagnosis of malignancy in thyroid nodules (TNs) with Bethesda Classification (BC) III or IV indeterminate cytology. This preliminary single-center prospective study evaluated 151 consented patients with 151 indeterminate TNs (123 BC III, 28 BC IV) on fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB). B-mode ultrasound, vascularity, and SWE were performed prior to FNAB. TN stiffness was measured as shear wave velocity (SWV) in meters per second (m/s). The stiffest area of the TN was selected for SWV measurement. GEC testing was performed with a second FNAB. Surgery was recommended for GEC-suspicious TNs, or GEC-benign TNs with two or more worrisome B-mode US features. Surgical pathology confirmed 31 malignant TNs. This preliminary study indicates that SWE and GEC are independent predictors of malignancy in TNs with BC III or IV.
read full article

Elastography is a new ultrasound technology that has the potential to help distinguish benign from malignant thyroid nodules. In this book chapter, Dr. Azizi and Dr. Malchoff review both strain and shear wave elastography: from exam performance techniques to spectacular case examples to recent research. Both technologies improve risk stratification in thyroid nodules when added to B-mode ultrasound exam, which could lead to fewer invasive procedures and surgeries.
read full article
This study prospectively determines the shear wave elastography characteristics of parathyroid adenomas using virtual touch imaging quantification, a non-invasive ultrasound based shear wave elastography method. This prospective study examined 57 consecutive patients with biochemically proven primary hyperparathyroidism and solitary parathyroid adenoma identified by ultrasound and confirmed by at least one of the following: surgical resection, positive Technetium–99 m Sestamibi Scintigraphy (MIBI) scan, or fine needle aspiration biopsy with positive PTH washout (performed only in MIBI negative patients).
read full article
This prospective study evaluates the accuracy of virtual touch imaging quantification (VTIQ), a non-invasive shear wave elastography method for measuring cervical lymph nodes (LN) stiffness in differentiating benign from malignant LN. The study evaluated 270 LN in 236 patients with both conventional B-mode ultrasound and VTIQ shear wave elastography before fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB).
read full article
This study determines the performance of virtual touch imaging quantification (VTIQ), a non-invasive shear wave elastography method for measuring thyroid nodule (TN) stiffness, in distinguishing benign from malignant TNs. This prospective study evaluates 707 TNs in 676 patients with fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB).
read full article
This prospective study investigates the relationship between Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (HT) and thyroid cancer (TC) in patients with thyroid nodules (TNs). We prospectively examined 2100 patients with 2753 TNs between January 5, 2010 and August 15, 2013. A total of 2023 patients with 2669 TNs met the inclusion criteria of TN >5 mm and age >18 years.
read full article
In the ultrasound evaluation of masses, elastography measures stiffness, which may predict malignancy. We prospectively tested the hypothesis that TN stiffness, as measured by strain elastography (SE), is an independent predictor of thyroid cancer (TC) in unselected TNs.In 706 unselected patients with 912 TNs meeting the ATA criteria for a fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB), we first performed conventional thyroid ultrasound and SE.
read full article read full article
read full article

Objective: To examine the relationship between clinical markers of autoimmune thyroid disease and the risk of thyroid cancer in patients with thyroid nodules. A retrospective cohort analysis was performed in a single clinical practice. In 2,500 consecutive patients, fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) was performed on all 3,658 ultrasonography-positive thyroid nodules that were ≥1.0 cm in diameter or ≥0.5 cm in diameter with ultrasound features suspicious for thyroid cancer. Serum concentrations of thyroglobulin antibodies (TgAb), thyroid peroxidase antibodies, and thyroid-stimulating hormone were measured before FNAB. Diagnosis of thyroid cancer was based on pathologic analysis of thyroidectomy tissue. Associations of thyroid cancer with the independent variables were determined by multivariate logistic regression analysis and reported as the adjusted odds ratio (OR) with the 95% confidence interval (CI).
read full article

PURPOSE: To determine whether daily oral micronized progesterone affects bone turnover, as estimated by serum and urine biochemical markers, in postmenopausal women on long-term estrogen replacement therapy (ERT).We recruited 14 women aged 65 or older to participate in a 9-week trial with micronized progesterone. Each woman had undergone a hysterectomy and was on unopposed ERT at time of study entry. Women received micronized progesterone 100 mg twice daily in the first week and then received 200 mg twice daily in weeks 2-9. We measured markers of bone turnover in serum and urine collected at baseline and at 3 weeks, 6 weeks, and 9 weeks on treatment.
read full article read full article
read full article